User Guide
About FoodRem
FoodRem is an Inventory Management System that empowers small food and beverage (F&B) restaurant managers to manage inventory and obtain insights from inventory data. As a restaurant manager, you can easily view and edit your inventory during your daily operations. Utilize FoodRem’s flexible tagging system to help you organize your inventory according to your business needs. Finally, streamline your business decisions by deriving insights from your inventory usage through FoodRem’s statistics – you can keep track of metrics such as food wastage amount if you wish!
TIP
For a more detailed view of FoodRem’s features, you can refer to the Features section below!
With a focus on efficiency, you can interact with FoodRem without ever reaching for your mouse or moving away from your keyboard! With a focus on user-friendliness, FoodRem is easy to learn!
This User Guide provides an in-depth documentation so you can easily use and integrate FoodRem into your day-to-day inventory management operations. It covers how to launch FoodRem, core FoodRem features and commands, common terms and definitions used in FoodRem, and some troubleshooting recommendations. Head over to How to use the User Guide to get started!
Table of Contents
- About FoodRem
- Table of Contents
- Features
- How to use the User Guide
- Installation
- Quick Reference Guide
- Commands
- Item Commands
- Create a new item:
new - Search for an item:
find - List all items:
list - Sort all items by an attribute:
sort - View the information of an item:
view - Increment the quantity of an item:
inc - Decrement the quantity of an item:
dec - Edit the information of an item:
edit - Add a remark to an item:
rmk - Delete an item:
del
- Create a new item:
- Tag Commands
- Statistics Command
- General Commands
- Item Commands
- Command Summary
- Troubleshooting
- FAQ
- Acknowledgements
- Glossary
Features
There are two core features that FoodRem provides:
- Inventory Management System
- Inventory Analysis Tool
Inventory Management System
FoodRem allows you to track your inventory during your daily operations.
- Quickly create, view, edit, and remove your available inventory.
- Sort your inventory items by name,
quantity
The amount/count of item(s) kept track by FoodRem.
Click to view glossary , unit, bought date Date where an item was purchased. Bought date is in the format “day-month-year”, represented in the “dd-mm-yyyy” format.
Click to view glossary , expiry date Date where an item spoils, expires, or becomes unusable. Expiry date is in the format “day-month-year”, represented in the “dd-mm-yyyy” format.
Click to view glossary , price and remarks. - Tag
items
Represents a thing that is stored and kept track by FoodRem.
Click to view glossary in your inventory using an efficient tagging system where you can create, rename and delete existing tags The main method of categorizing items in FoodRem. A tag may be attached to zero or more items.
Click to view glossary . - Filter your inventory items by item name and tag.
WARNING
FoodRem can only hold up to 10,000 items and 100 tags!
Inventory Analysis
FoodRem tracks data that helps you streamline your business decisions through statistics:
- Find out how much cost was incurred due to food wastage.
- Track your top 3 most expensive items.
- View your items that are expiring soon.
How to use the User Guide
Thank you for choosing FoodRem! We are delighted to have you as a user and we aim to serve you and your business well!
INFO
We highly recommend that you read through the User Guide in a sequential order. Please note the importance of the Quick Reference Guide section, which covers how to use FoodRem!
TIP
This User Guide is highly navigable; simply click on any item in the Table of Contents and be directed to it! Clicking on the respective headings will bring you back to the Table of Contents, so it’s easy to jump across sections!
If you have not installed FoodRem head over to the Installation section.
Once FoodRem is installed, you can head over to the section Quick Reference Guide which covers the basics of using FoodRem. This includes:
- FoodRem’s Layout
- What Items and Tags are in FoodRem
- What Flags and Placeholders are
- FoodRem’s Command format
- Trying out your first FoodRem command
If you are an experienced user, you can refer to the Command Summary for a quick overview of all of FoodRem’s commands.
If you are stuck, refer to the section on Troubleshooting or FAQ.
You can also refer to the Glossary for definitions of commonly used terms in FoodRem.
Admonition Boxes
Throughout this guide, you may find coloured boxes containing highlighted pieces of text. These are known as admonition boxes, or simply,
admonitions
Admonition boxes (or simply “admonitions”) are coloured boxes containing highlighted pieces of text.
Click to view glossary
. Please take note of the content within.
| Icon | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Something you should keep in mind. | |
| Something you might find useful. | |
| Something that provides information useful in that context. | |
| Something you should be cautious about. | |
| Something you should pay a lot of attention to. |
Other Notation
Besides icons, there are also some special notations that are used in this guide:
- Links in blue point to other sections in this document, or places on the internet.
- Words with a dotted underlineA summary of the glossary entry will appear here. represent terms, which when clicked, take you to the corresponding entry in the glossary section at the end of this guide.
Installation
If you haven’t installed FoodRem, simply follow these steps to set it up:
- Download and install Java 17 on your computer
- Download the latest
foodrem.jarfile from our releases page - Copy the jar file to an empty folder. This will be your home folder for FoodRem
- Double-click on the jar file to launch FoodRem
WARNING
Remember to add foodrem.jar into an empty folder as additional data and configuration files will be created when launching FoodRem for the first time!
Congratulations! You now have FoodRem set up.
DANGER
When you launch FoodRem, notice that you will have a folder called “data” that is created in the same folder as foodrem.jar. Editing the file might corrupt your data, avoid doing this unless you know what you are doing!
Quick Reference Guide
This section covers all you should know about FoodRem, as well as a guided tutorial. Of special note is the Key Definitions and Command Format sections, which covers essential knowledge to using FoodRem’s features.
Layout
When you launch FoodRem, FoodRem appears on your screen as a
Graphical User Interface
A Graphical User Interface is a graphics-based interface that uses icons, menus and a mouse (to click on the icon or pull down the menus) to manage interaction with the system. In FoodRem, this presents as the window that appears when launching it.
Click to view glossary
, or GUI. Let’s look at the layout of the different components of FoodRem.
FoodRem’s GUI consists of a single main window, as well as the
Help Window
A pop-up window containing help information, shown only after calling a help command.
Click to view glossary
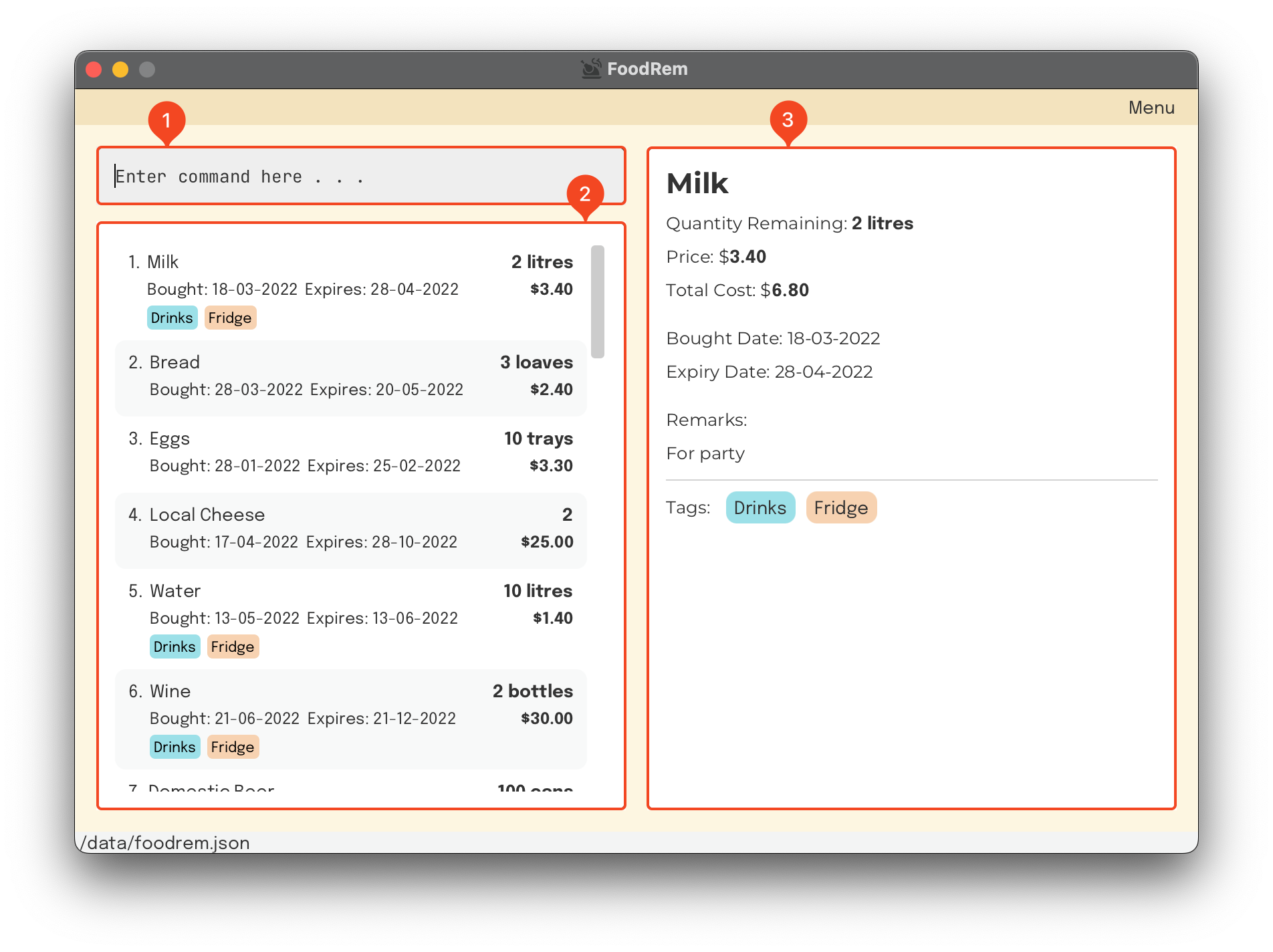
. The main window consists of three components:
- Command Input Box
- Item List Box
- Command Output Box
The following picture of the main window shows the three components, numbered accordingly:
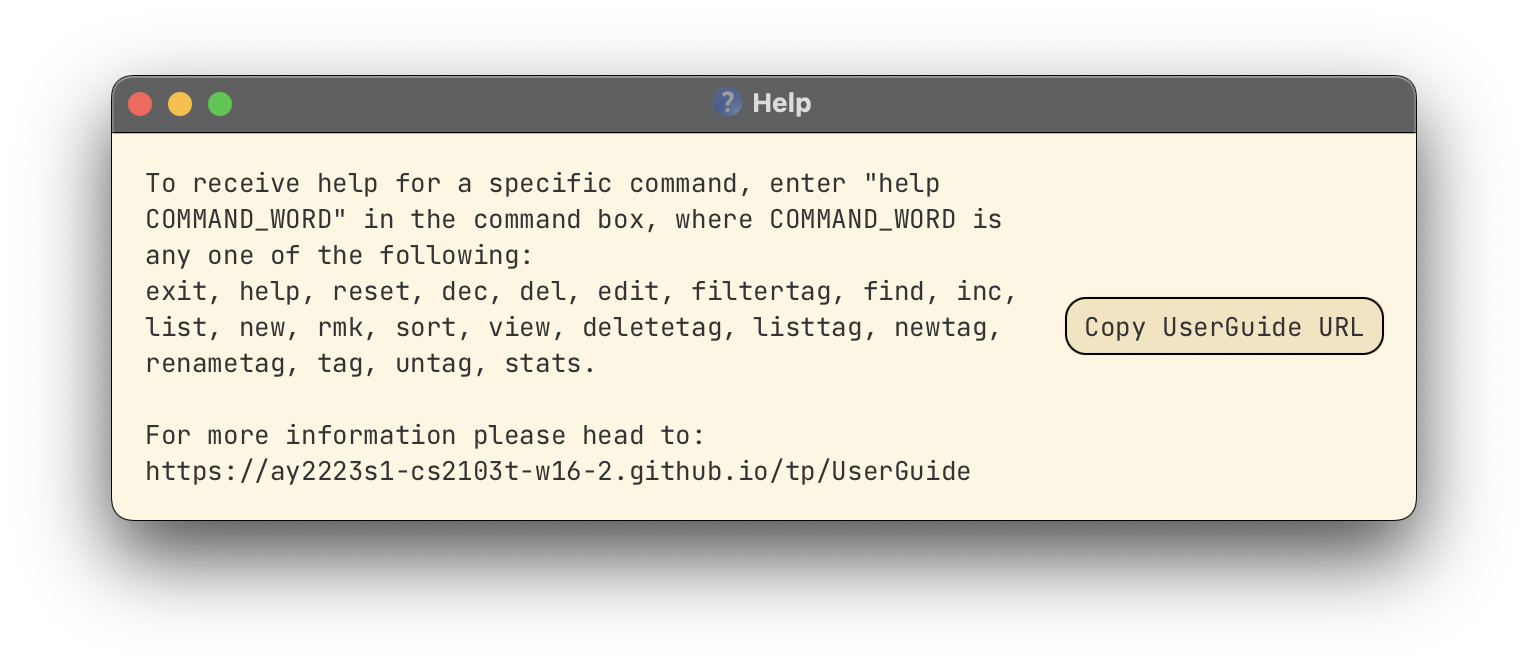
Besides the main window, FoodRem also has the Help Window. It is not part of the main GUI and is only shown after a Help Command is run.
The Help Window looks like the following:
Key Definitions
Item
An
Item
Represents a thing that is stored and kept track by FoodRem.
Click to view glossary
in FoodRem represents something in your inventory. This can be an ingredient, a piece of equipment, and more. Feel free to include or exclude certain attributes for each item, although you must minimally provide a name for the item.
The following are the attributes stored for each item:
- Item name
- Item
quantity
The amount/count of item(s) kept track by FoodRem.
Click to view glossary - Item unit (unit of measurement e.g.
kg,packets) - Item
bought date
Date where an item was purchased. Bought date is in the format “day-month-year”, represented in the “dd-mm-yyyy” format.
Click to view glossary - Item
expiry date
Date where an item spoils, expires, or becomes unusable. Expiry date is in the format “day-month-year”, represented in the “dd-mm-yyyy” format.
Click to view glossary - Item price
- Item remarks
- Item
tags
The main method of categorizing items in FoodRem. A tag may be attached to zero or more items.
Click to view glossary
FoodRem Items are unique by name and case-sensitive. This means you cannot add two or more items of the same name.
Restrictions for all attributes can be found in the Placeholders section.
Tag
A Tag in FoodRem serves as a means to categorise and filter items. These tags are also unique and case-sensitive.
We can tag multiple items with the same tag and each item can have multiple tags. These Tags are optional.
Feel free to add tags as you see fit to organize your inventory. Examples of how you may use a tag can include:
- Categorizing food items, e.g.
Vegetable,Herb,Condiment,Meat - Marking where the item is stored, e.g.
Fridge,Cupboard,Shelf - Noting its perishability, e.g.
Perishable,Non-Perishable
Tags can be renamed and these changes would be reflected on all items immediately.
FoodRem Tags are unique by name and case-sensitive. This means you cannot add two or more tags of the same name.
Flags
Flags are
delimiters
A sequence of one or more characters for specifying the boundary between separate, independent regions in plain text.
Click to view glossary
that enable FoodRem to distinguish different
parameters
Parameters identify values passed into your Commands. For example, when calling add n/ItemName, the parameter here is n/ItemName.
Click to view glossary
without ambiguity.
You would put in the corresponding Placeholder immediately after each flag.
Please refer to the subsequent Command Format section to see how Flags and Placeholders are used together.
| Flag | Corresponding Placeholder |
|---|---|
| n/ | ITEM_NAME TAG_NAME |
| qty/ | QUANTITY |
| u/ | UNIT |
| bgt/ | BOUGHT_DATE |
| exp/ | EXPIRY_DATE |
| p/ | PRICE |
| r/ | REMARKS |
Placeholders
Placeholders in this User Guide refers to the UPPER_CASE words that can be replaced by valid user input supplied. These placeholders follow immediately after a Flag.
Please refer to the subsequent Command Format section to see how Flags and Placeholders are used together.
NOTE
The placeholders INDEX, COMMAND_WORD, and KEYWORD do not have any corresponding flags. They are marked as “Not Applicable” in the table below.
| Placeholder | Corresponding Flag | Description |
|---|---|---|
| INDEX | (Not Applicable) |
The INDEX of an item is the number to the left of the item name in the Item List Box. INFO
Valid Examples:
Invalid Examples:
|
| ITEM_NAME | n/ |
The ITEM_NAME is the name we use to identify an item. INFO
Valid Examples:
Invalid Examples:
|
| TAG_NAME | n/ |
The TAG_NAME is the term we use to identify an item. INFO
Valid Examples:
Invalid Examples:
|
| QUANTITY | qty/ |
The QUANTITY is the number representing the amount of an item. INFO
Valid Examples:
Invalid Examples:
|
| UNIT | u/ |
The UNIT is a text indicating the unit-of-measurement of an item. INFO
Valid Examples:
Invalid Examples:
|
| BOUGHT_DATE | bgt/ |
The BOUGHT_DATE is the date indicating when an item was bought. INFO
Valid Examples:
Invalid Examples:
|
| EXPIRY_DATE | exp/ |
The EXPIRY_DATE is the date indicating when an item will expire. INFO
Valid Examples:
Invalid Examples:
|
| PRICE | p/ |
The PRICE is the number representing the cost of one unit of an item. INFO
Valid Examples:
Invalid Examples:
|
| REMARKS | r/ |
The REMARKS of an item is a note that you can add to an item. INFO
Valid Examples:
INVALID EXAMPLES:
|
| COMMAND_WORD | (Not Applicable) |
The COMMAND_WORD is a text indicating a command word of a command. Refer to the Command Format for more info. INFO
Valid Examples:
Invalid Examples:
|
| KEYWORD | (Not Applicable) |
The KEYWORD is the text we use to search for an item. INFO
Valid Examples:
Invalid Examples:
|
Command Format
You will encounter FoodRem
commands
A feature or function that FoodRem can perform.
Click to view glossary
throughout this User Guide. Before you delve into the different commands in Commands, let’s learn what a command consists of.
Here is an example:
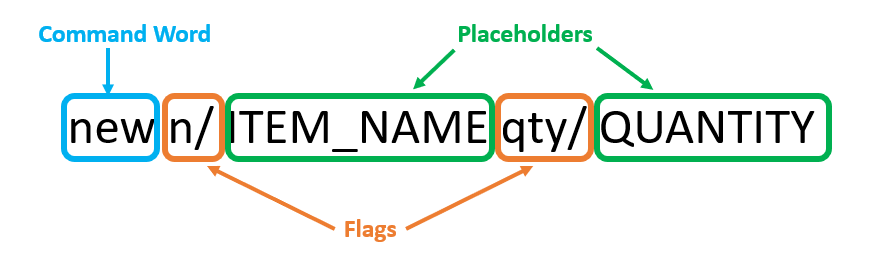
A command consists of:
- Command Word: Tells FoodRem what action you wish to execute. These actions are covered in Commands.
- Flags: Distinguishes between inputs. A flag is usually followed by a placeholder.
- Placeholders: Represents data that you wish to input. Replace this with valid data. For example,
ITEM_NAMEinn/ITEM_NAMEcan be replaced withn/Potato.
Trying your first command
To let you become more familiar with FoodRem, let’s practice executing some
commands
A feature or function that FoodRem can perform.
Click to view glossary
.
To start off, let’s try out the new command! This command lets you add an Item to FoodRem.
One of the available commands in FoodRem is the command to create a new item.
Format: new n/ITEM_NAME [qty/QUANTITY] [u/UNIT] [bgt/BOUGHT_DATE] [exp/EXPIRY_DATE] [p/PRICE] [r/REMARKS]
What does the format mean?
The first word of every command allows FoodRem to distinguish different commands.
newtells FoodRem that this is the command to create a new item- Flags such as
n/andqty/are delimiters A sequence of one or more characters for specifying the boundary between separate, independent regions in plain text.
Click to view glossary that enable FoodRem to distinguish different parameters Parameters identify values passed into your Commands. For example, when calling add n/ItemName, the parameter here is n/ItemName.
Click to view glossary supplied by you without ambiguity - Placeholders such as
ITEM_NAMEandQUANTITYshows you what you should place in each portion of the command
Notice that there is a pair of square brackets [] surrounding some
parameters
Parameters identify values passed into your Commands. For example, when calling add n/ItemName, the parameter here is n/ItemName.
Click to view glossary
like qty/QUANTITY in the format. This indicates that the parameter is optional. Each of these
placeholders
Placeholders in FoodRem refers to the UPPER_CASE words that appear after flags in commands that can be replaced by user input supplied. For example in n/ITEM_NAME, ITEM_NAME is a placeholder.
Click to view glossary
in the
parameters
Parameters identify values passed into your Commands. For example, when calling add n/ItemName, the parameter here is n/ItemName.
Click to view glossary
have a default value based on the commands. These are documented in the Commands section for each command.
NOTE
The Placeholder section covers the restrictions for respective placeholders. For example, the date format of BOUGHT_DATE, certain characters you cannot use and the limit and precision of numbers.
Let’s try an example!
Suppose you just bought 30 kg worth of potatoes, today is 5th September 2022, and you do not feel the need to record an
expiry date
Date where an item spoils, expires, or becomes unusable. Expiry date is in the format “day-month-year”, represented in the “dd-mm-yyyy” format.
Click to view glossary
, price or remarks for this item.
ITEM_NAME: Potatoes
QUANTITY: 30
UNIT: kg
BOUGHT_DATE: 05-09-2022
The command you would like to enter into the command box would be:
new n/Potatoes qty/30 u/kg bgt/05-09-2022
Alternatively, executing these would do the same thing:
-
new qty/30 n/Potatoes bgt/05-09-2022 u/kgThis is because the order of the flags does not matter.
-
new qty/100 n/Carrots qty/30 n/Potatoes bgt/05-09-2022 u/kgIf two or more values of the same parameter Parameters identify values passed into your Commands. For example, when calling add n/ItemName, the parameter here is n/ItemName.
Click to view glossary are provided, only the last value for that parameter will be taken. In this case, the name “Carrots” will be overridden by “Potatoes”, and the quantity “100” will be overridden by “30”.
However, note that the following executions are invalid:
-
newn/Potatoesqty/30u/kgbgt/05-09-2022There must be between the placeholders and flags.
-
new qty/-48 n/PÖtátÖes bgt/05/09/22 u/|kg|The restrictions of placeholders are not followed.
-
newThere is insufficient information provided; you must minimally provide a name.
Find out more about restrictions in the sections Flags, Placeholders and Commands.
Let’s try out another command – the inc command! inc lets you increment the quantity of an item.
WARNING
The format for different commands are not always identical. For example, executing the new command and the inc command will have different formats!
For example, after creating the potatoes item, you decided to buy 40 kg more of potatoes.
Format: inc INDEX [qty/QUANTITY]
Suppose the INDEX for potatoes is 1 in the application, the command you would like to enter into the Command Input Box would be:
inc 1 qty/40
You should now have a better understanding of how commands are formatted and used. All commands are consolidated in the Command Summary.
Here is a checklist you can use before running a
command
A feature or function that FoodRem can perform.
Click to view glossary
:
- I know the restrictions of the command
- I know what
parameters
Parameters identify values passed into your Commands. For example, when calling add n/ItemName, the parameter here is n/ItemName.
Click to view glossary are supplied to the command - I know the
flags
A marker or delimiter signifying a potentially optional argument to a command. For example on FoodRem, in the syntax n/ITEM_NAME , n/ is the flag.
Click to view glossary for each parameter to be supplied - I know the restrictions of each parameter
- I know the effects of not specifying each optional flag.
Commands
This section shares with you on how to use each
command
A feature or function that FoodRem can perform.
Click to view glossary
in detail.
Before continuing, ensure you have read the section on Flags and Placeholders.
What you should expect to find:
- A description of the command
- The format of the command
- The expected behaviour of the command
- A few valid and invalid examples of the command
- Important points to note
NOTE
- For each command, “Format” indicates the syntax of the command.
- Square brackets indicates an optional
parameter
Parameters identify values passed into your Commands. For example, when calling add n/ItemName, the parameter here is n/ItemName.
Click to view glossary . - In most commands, if the same parameter is repeated and only one is required, we take the last value provided.
Item Commands
Example of an Item:

Create a new item: new
Format: new n/ITEM_NAME [qty/QUANTITY] [u/UNIT] [bgt/BOUGHT_DATE] [exp/EXPIRY_DATE] [p/PRICE] [r/REMARKS]
Creates a new item with the provided information
INFO
- All fields apart from
ITEM_NAMEare optional. - The
BOUGHT_DATEshould not be after theEXPIRY_DATE. - The format for
BOUGHT_DATEandEXPIRY_DATEshould follow: “dd-mm-yyyy”.- “dd”: Day of the month. For example, “10” would represent the 10th day of the month.
- “mm”: Month of the year, ranging from 1 to 12 for January to December respectively. For example, “05” would represent May.
- “yyyy”: A 4-digit year. For example, “2019” would represent the year 2019.
- The value of
BOUGHT_DATE,EXPIRY_DATEwill beNot Setif it is not provided. - The default value for
QUANTITYandPRICEis0. - The default value for
UNITis blank. - The value of
REMARKSwill be-if is it not provided. PRICEdoes not require you to include the currency. Only include the value.
NOTE
- You cannot create an item and tag it at the same time.
- If two or more values of the same
parameter
Parameters identify values passed into your Commands. For example, when calling add n/ItemName, the parameter here is n/ItemName.
Click to view glossary are provided, only the last value for that parameter will be taken.
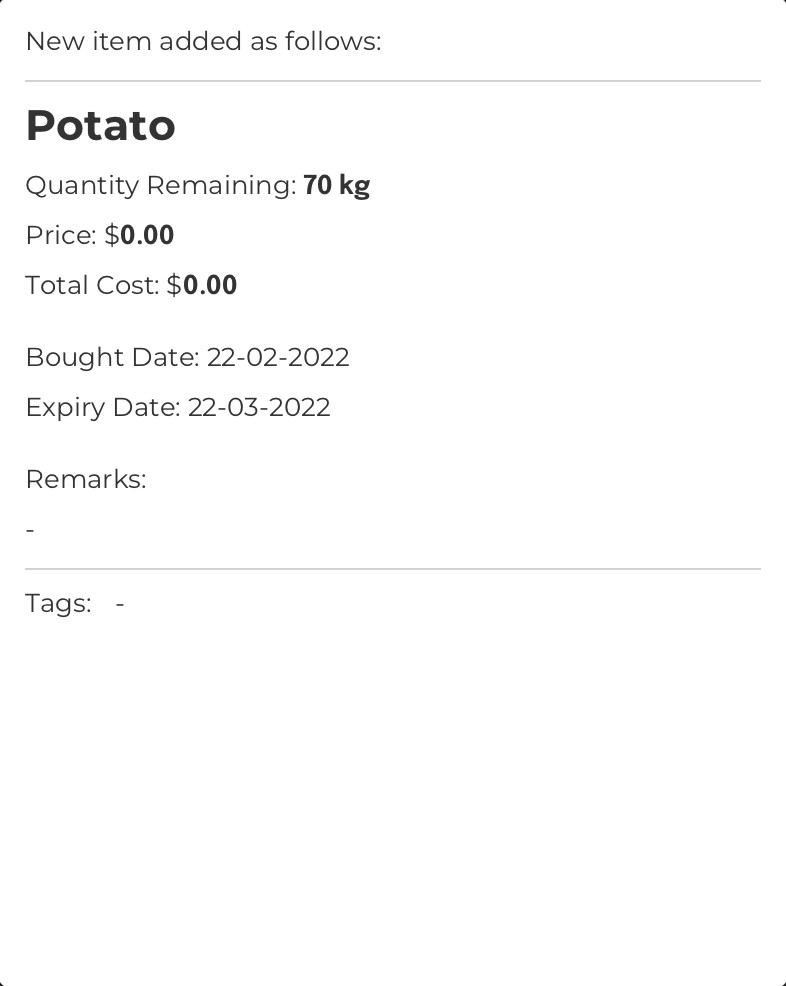
Example:
Command Input Box:
new n/Potato qty/70 u/kg bgt/22-02-2022 exp/22-03-2022
Assumption:
FoodRem does not already contain an item with the name “Potato”.
Search for an item: find
Format: find KEYWORD [KEYWORDS]...
Finds all items in FoodRem whose names contain substrings A contiguous sequence of characters (letters) that form a part (or a whole) string of text.
Click to view glossary of the KEYWORDS
INFO
- The notation
[KEYWORDS]...means that we can take in multiple keywords. In this case, at least oneKEYWORDis required. - The
KEYWORDSare case-insensitive. (e.g. “apples” will match “Apples”). - The result will be items where each of the
KEYWORDSare present in theITEM_NAMEas a substring. (e.g. “c e” will match “Carrot Cake”, “cereal”, “Cold Escargo” and “eclairs”)
TIP
- You can use the List Command in the next section to display all items again!
NOTE
- The
findcommand only findsItemswhich has a name that partially or fully matches the specified search by name! - This means that if the
ItemsBrown SugarandWhite Sugaris in FoodRem, executingfind Sugarwill find these twoItems. - However, if you try to find an
ItemPotatoby executing the commandfind potatoes carrots celery, it will not work!
Example:
Command Input Box:
find b sug
Assumption:
Initially, FoodRem only contains the following items:
- Sugarcane Juice Box
- Brown Sugar
- Tomato
- Carrot

List all items: list
Format: list
List all items in FoodRem
INFO
- This command is useful to view all items again after using the Find Command.
Example:
Command Input Box:
list
Assumption:
FoodRem contains the following items, each with their own attributes:
- Sugarcane Juice Box
- Brown Sugar
- Tomato
- Carrot
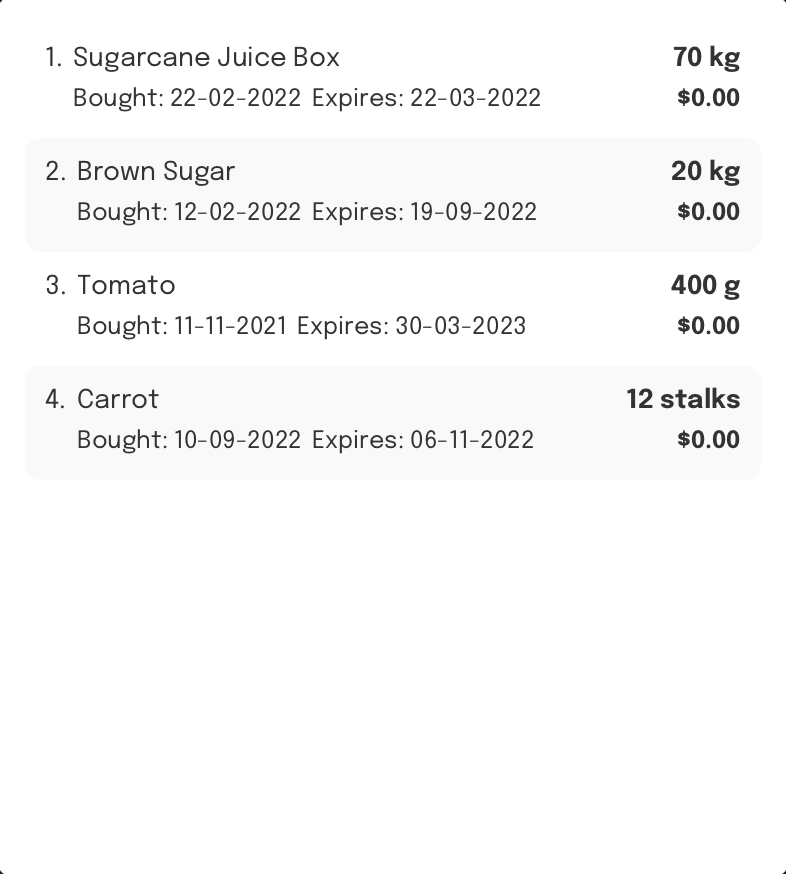
Sort all items by an attribute: sort
Format: sort [n/] [qty/] [u/] [bgt/] [exp/] [p/] [r/]
Sorts the list of currently displayed items by the provided criteria
NOTE
sort n/: Sort by item namesort qty/: Sort by item quantitysort u/: Sort by item unitsort bgt/: Sort by item bought datesort exp/: Sort by item expiry datesort p/: Sort by item pricesort r/: Sort by item remarks
TIP
You may find this command useful when you need to quickly dispose of expiring items or to check item stocks, but the sky is the limit! You can use FoodRem in creative ways to take advantage of this! For example, if you use the PRICE field to store each item’s profit per unit sold, you can use this command to see which items are giving you the most profits!
WARNING
- You should only provide one sorting criteria.
- The sort can only be done in ascending order.
Example:
Command Input Box:
sort n/
Assumption:
FoodRem contains the following items:
- Sugarcane Juice Box
- Brown Sugar
- Tomato
- Carrot
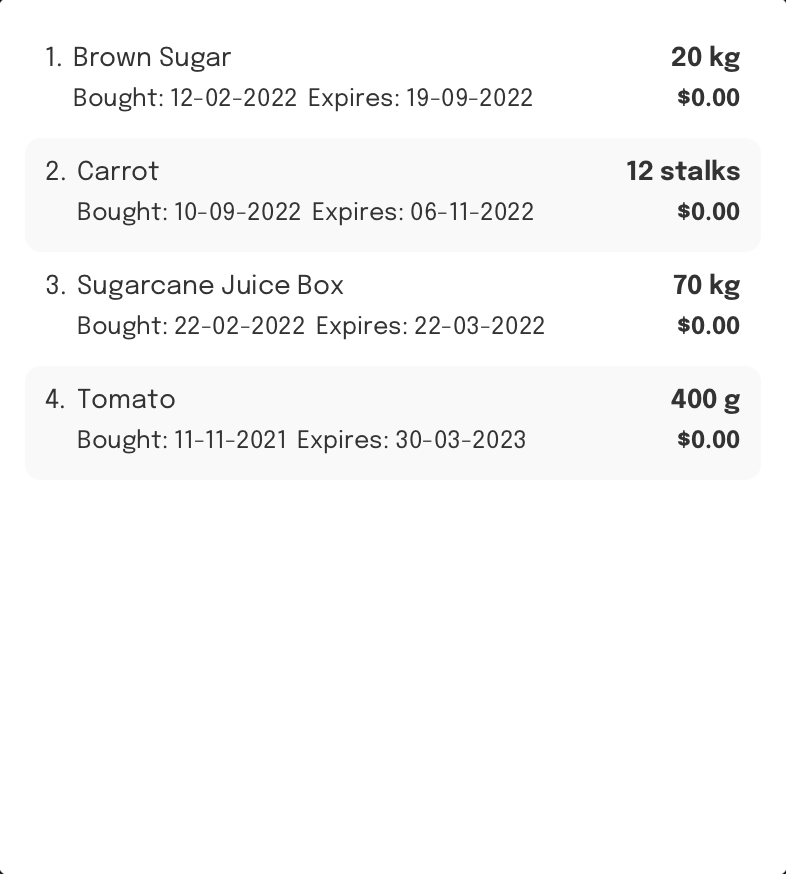
View the information of an item: view
Format: view INDEX
Displays the item at the specified index
INFO
- Displayed information includes the name, quantity, unit, bought date, expiry date, price, remarks and tags of items.
Example:
Command Input Box:
view 1
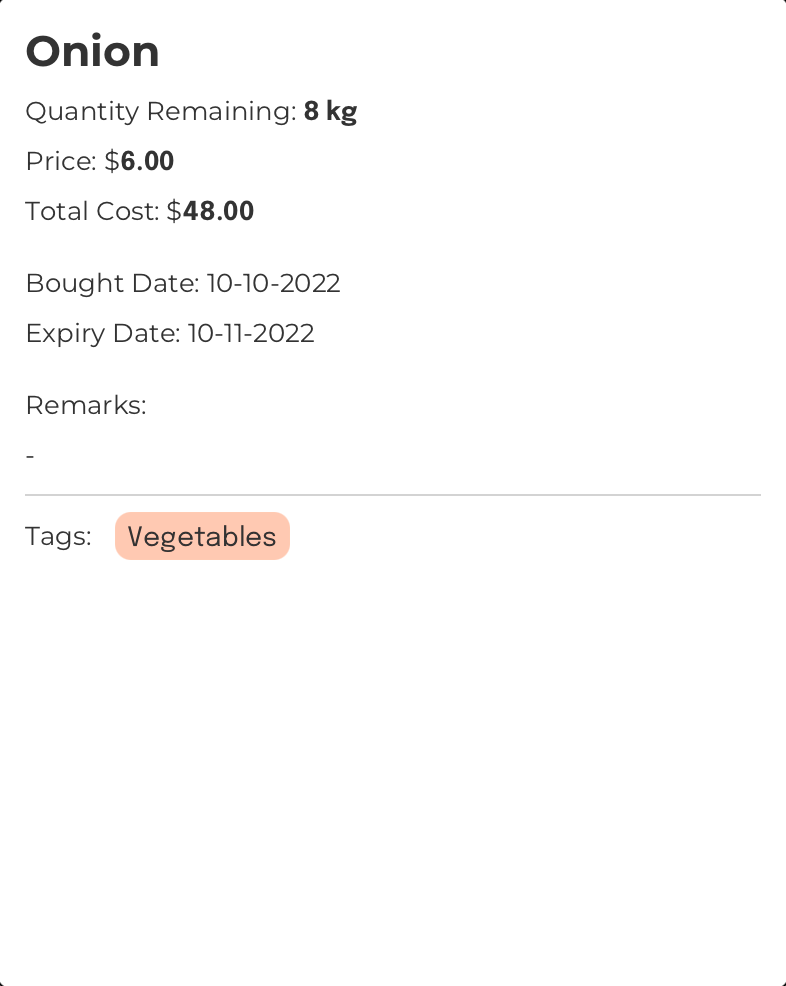
Assumption:
The currently displayed
Item List Box
The region located at the bottom-left of FoodRem’s main window.
Click to view glossary
in FoodRem shows the item named “Onion” at INDEX value 1.
The command will produce a detailed view of this item.
Increment the quantity of an item: inc
Format:: inc INDEX [qty/QUANTITY]
Increments the quantity of the item at the specified index
INFO
- If a quantity is not provided, the item quantity will be incremented by 1.
- If two or more
QUANTITYvalues are provided, only the lastQUANTITYwill be taken.
Example:
Command Input Box:
inc 1 qty/3
Assumptions:
- The currently displayed
Item List Box
The region located at the bottom-left of FoodRem’s main window.
Click to view glossary in FoodRem shows the item named “Onion” at INDEX value 1. - Initially, the “Onion” item has a “Quantity” of 8.
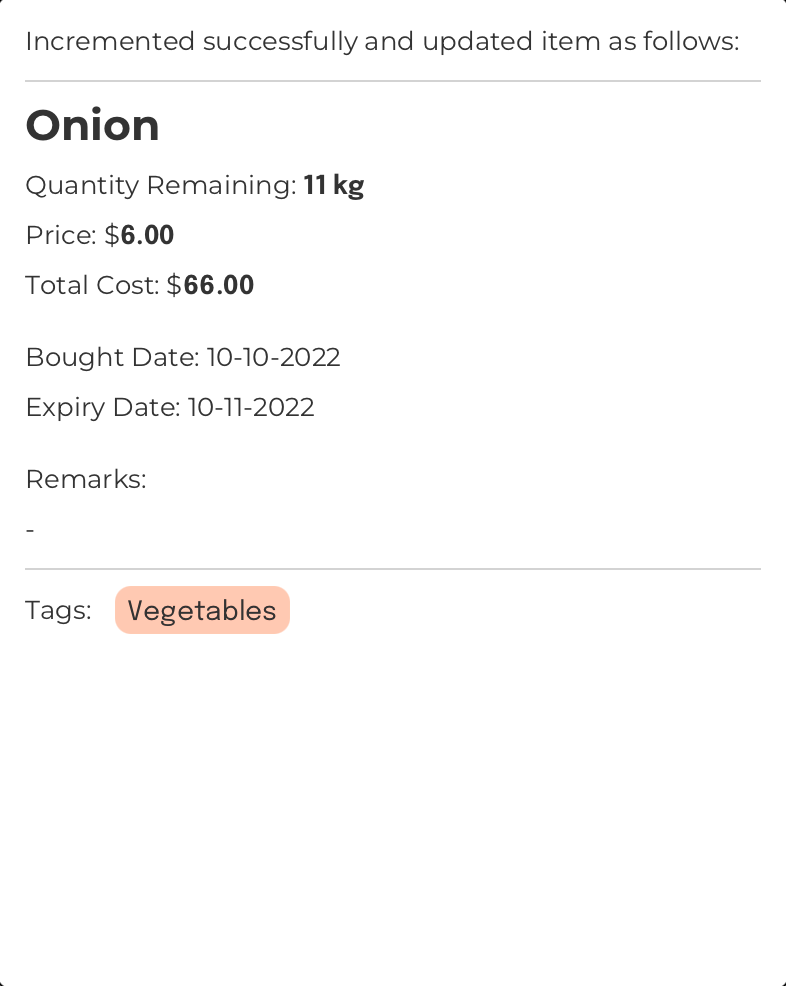
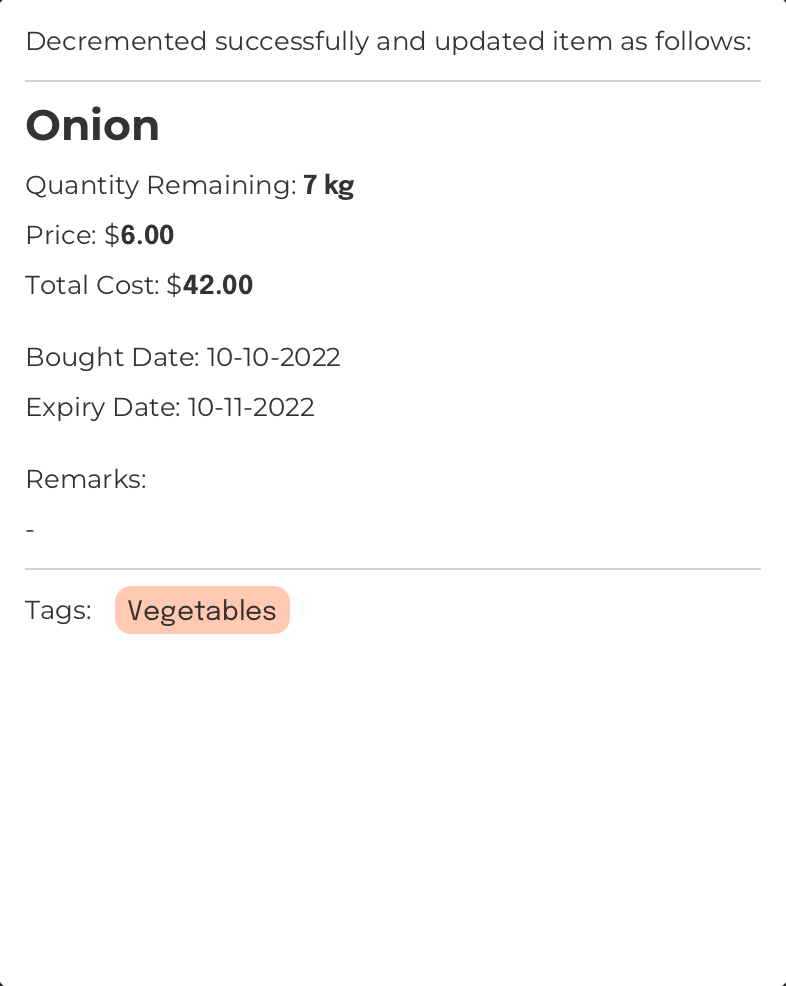
Decrement the quantity of an item: dec
Format:: dec INDEX [qty/QUANTITY]
Decrements the quantity of the item at the specified index
INFO
- If a quantity is not provided, the item quantity will be decremented by 1.
- If two or more
QUANTITYvalues are provided, only the lastQUANTITYwill be taken.
Example:
Command Input Box:
dec 1 qty/4
Assumptions:
- The currently displayed
Item List Box
The region located at the bottom-left of FoodRem’s main window.
Click to view glossary in FoodRem shows the item named “Onion” at INDEX value 1. - Initially, the “Onion” item has a “Quantity” of 11.
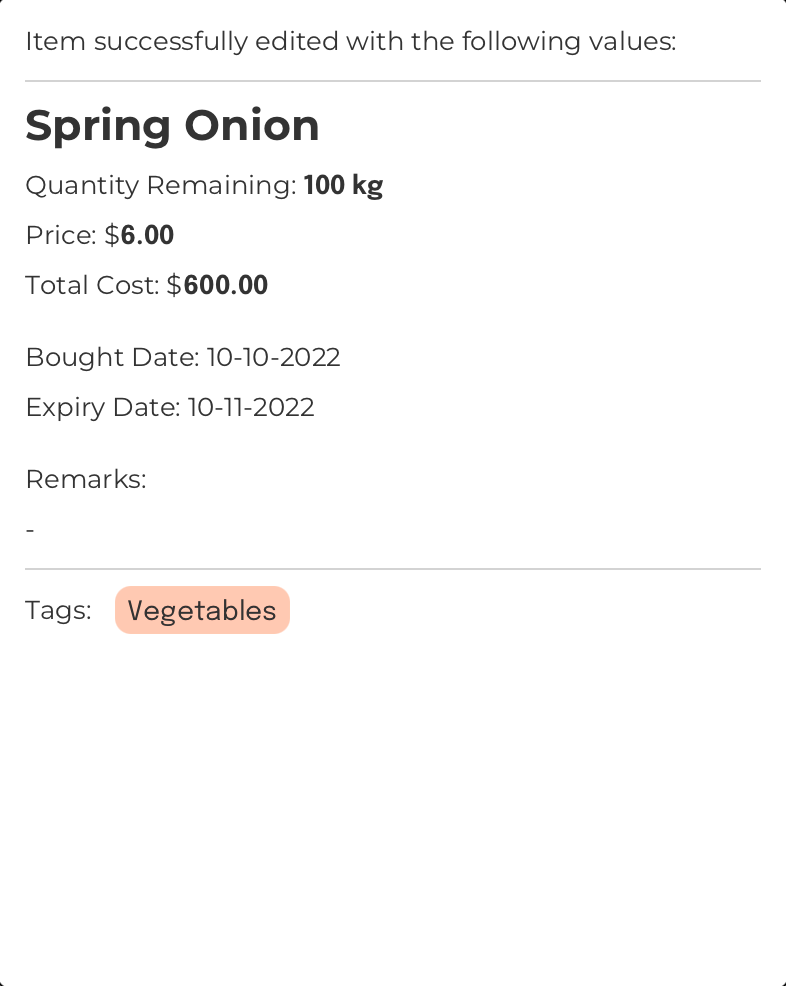
Edit the information of an item: edit
Format: edit INDEX [n/ITEM_NAME] [qty/QUANTITY] [u/UNIT] [bgt/BOUGHT_DATE] [exp/EXPIRY_DATE] [p/PRICE] [r/REMARKS]
Updates the details of the item at the specified index
INFO
- All fields are optional. However, you need to include at least one parameter.
- The
BOUGHT_DATEshould not be after theEXPIRY_DATE. - The format for
BOUGHT_DATEandEXPIRY_DATEshould follow: “dd-mm-yyyy”.- “dd”: Day of the month. For example, “10” would represent the 10th day of the month.
- “mm”: Month of the year, ranging from 1 to 12 for January to December respectively. For example, “05” would represent May.
- “yyyy”: A 4-digit year. For example, “2019” would represent the year 2019.
PRICEdoes not require you to include the currency. Only include the value.
NOTE
- If two or more values of the same
parameter
Parameters identify values passed into your Commands. For example, when calling add n/ItemName, the parameter here is n/ItemName.
Click to view glossary are provided, only the last value for that parameter will be taken.
Example:
Command Input Box:
edit 1 qty/100 n/Spring Onion
Assumptions:
- The currently displayed
Item List Box
The region located at the bottom-left of FoodRem’s main window.
Click to view glossary in FoodRem shows the item named “Onion” at INDEX value 1. - Initially, the “Onion” item has the following values:
- Unit: kg
- Bought Date: 10-10-2022
- Expiry Date: 10-11-2022
- Price: 6.00
- Remarks: -
- Tags: Vegetables
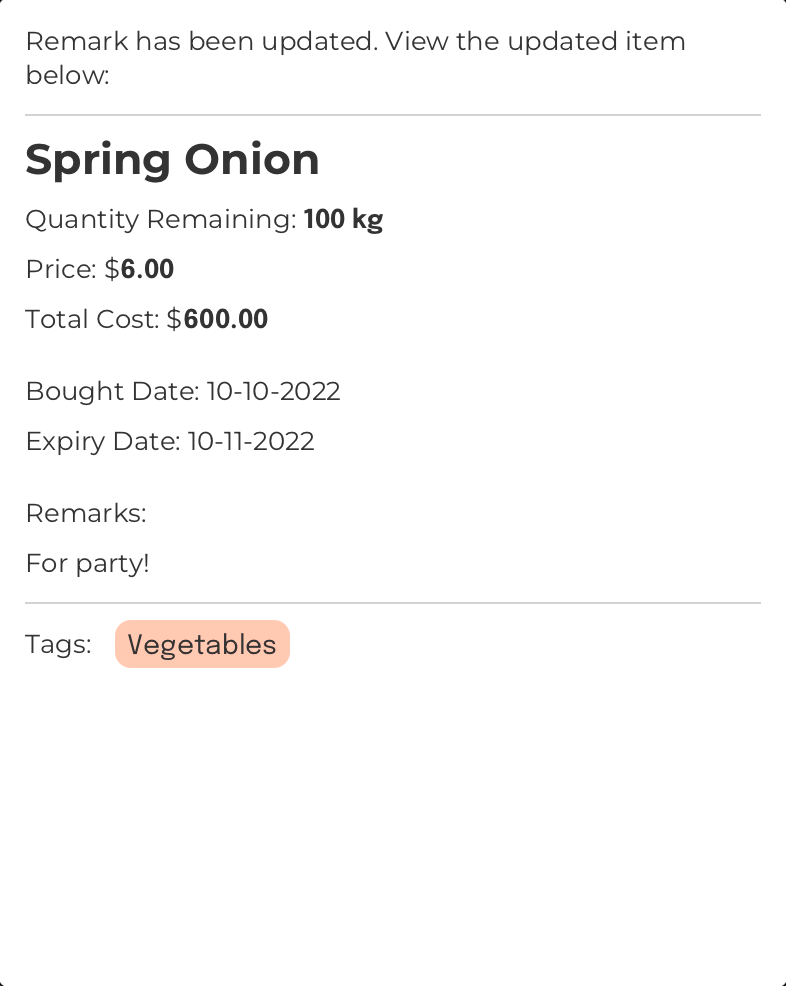
Add a remark to an item: rmk
Format: rmk INDEX [r/REMARKS]
Add a remark to the item at the specified index
INFO
- If no remark is provided, the current remark will be cleared.
- If two or more
REMARKSvalues are provided, only the lastREMARKSvalue will be taken. - If an item already has a remark, this command will overwrite the old remark with the new remark.
- The new remark can overwrite the old remark even if they are the same. This is to give the user flexibility in editing remarks.
Example:
Command Input Box:
rmk 1 r/For party!
Assumption:
The currently displayed
Item List Box
The region located at the bottom-left of FoodRem’s main window.
Click to view glossary
in FoodRem shows the item named “Onion” at INDEX value 1.
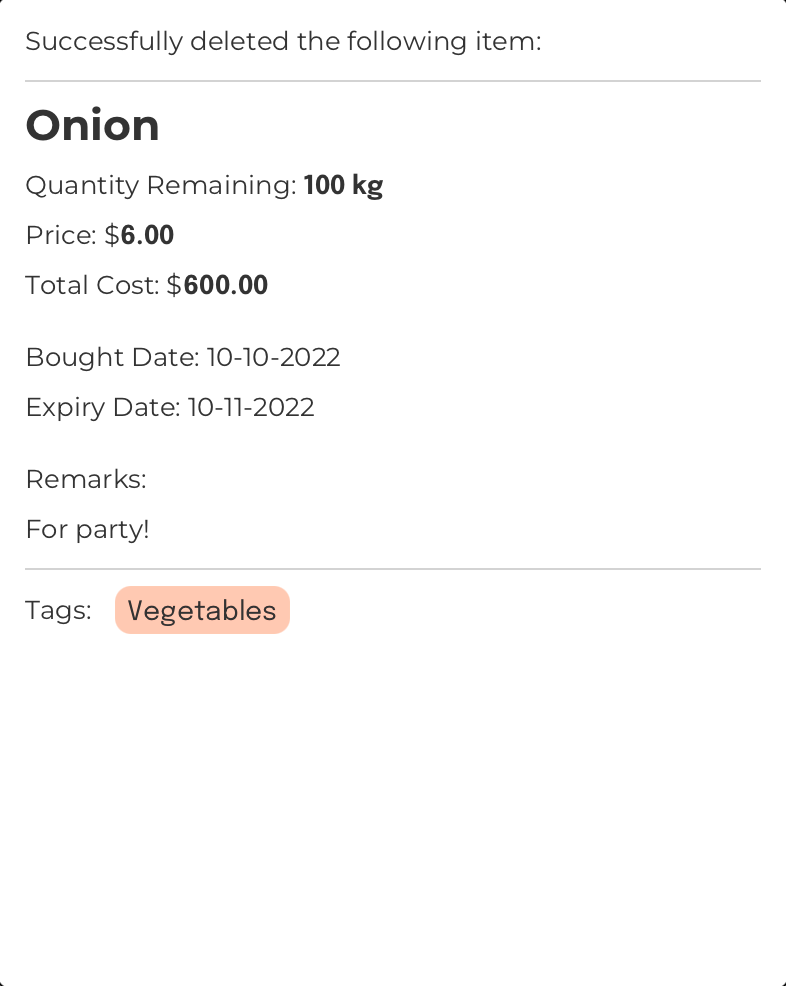
Delete an item: del
Format: del INDEX
Deletes the item at the specified index
Example:
Command Input Box:
del 1
Assumption:
The currently displayed
Item List Box
The region located at the bottom-left of FoodRem’s main window.
Click to view glossary
in FoodRem shows the item named “Onion” at INDEX value 1.
Tag Commands
Example of a Tag:

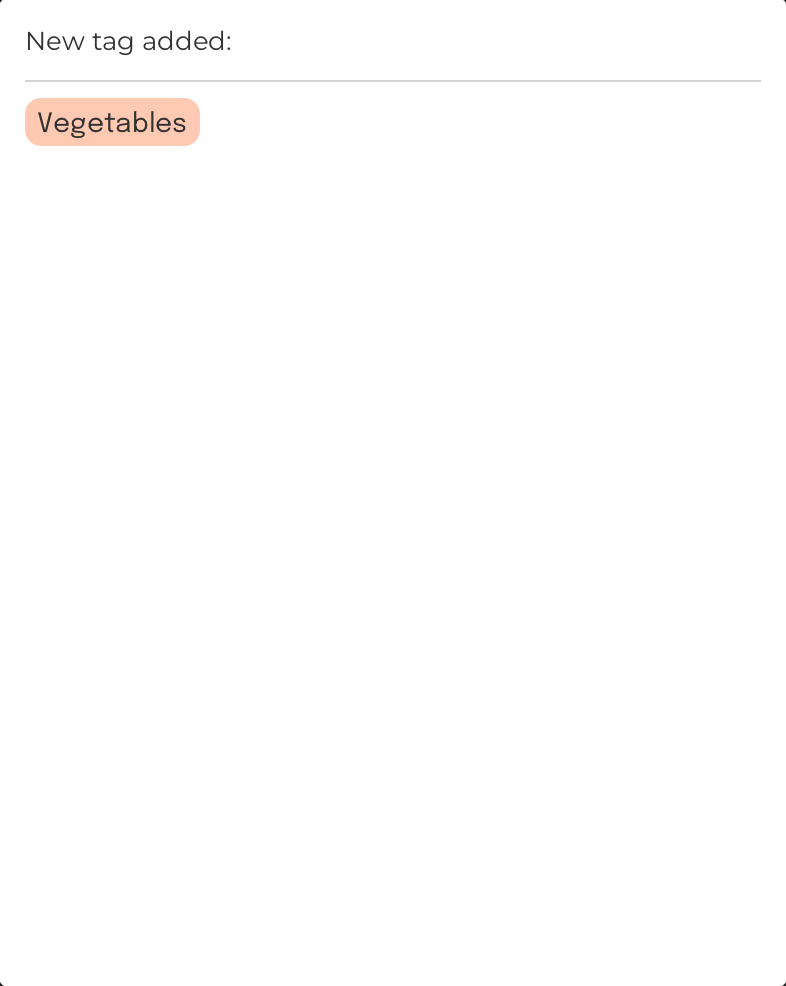
Create a new tag: newtag
Format: newtag n/TAG_NAME
Creates a new tag with the provided tag name
Example:
Command Input Box:
newtag n/Vegetables
Assumption:
FoodRem does not already contain a tag called “Vegetables”.
List all tags: listtag
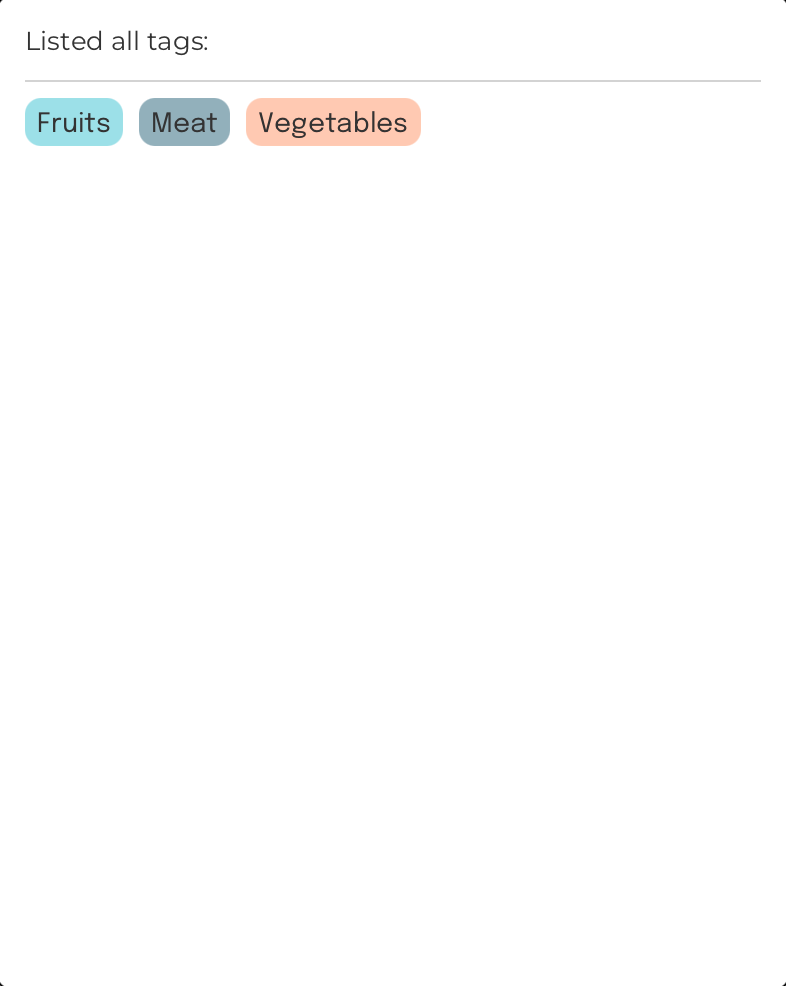
Format: listtag
List all tags in FoodRem
Example:
Command Input Box:
listtag
Assumption:
Initially, FoodRem contains only the following three tags:
- Fruits
- Meat
- Vegetables
Tag an item: tag
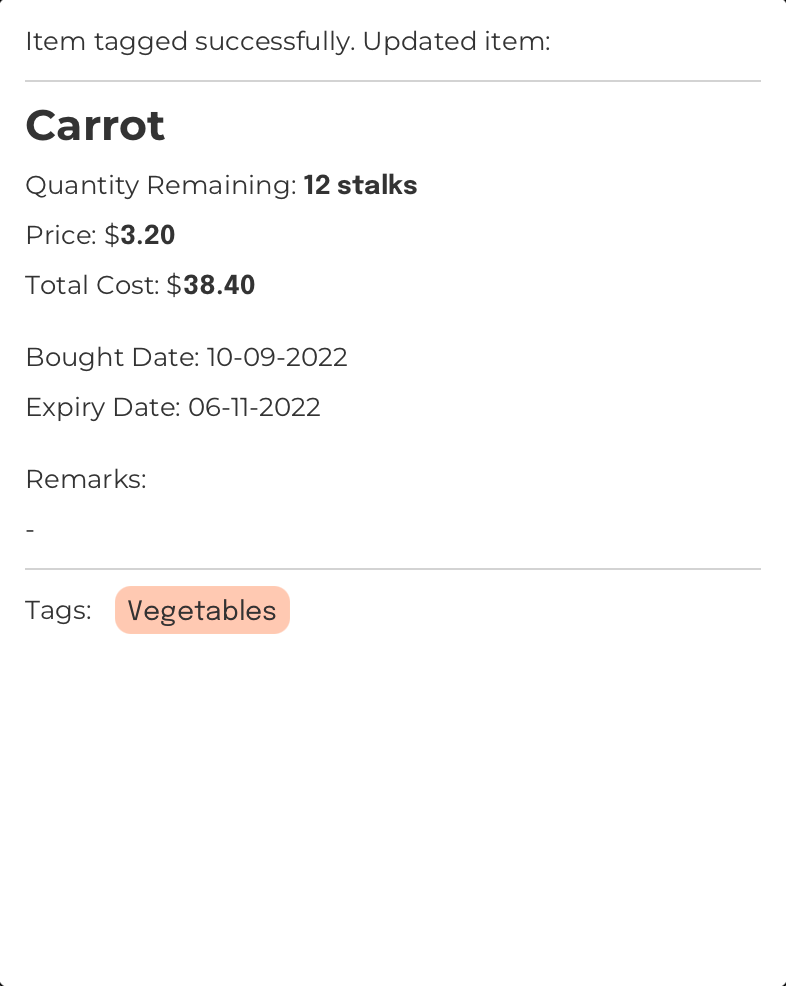
Format: tag INDEX n/TAG_NAME
Tags the item at the specified index
Example:
Command Input Box:
tag 1 n/Vegetables
Assumptions:
- The currently displayed
Item List Box
The region located at the bottom-left of FoodRem’s main window.
Click to view glossary in FoodRem shows the item named “Carrot” at INDEX value 1. - There exists a tag called “Vegetables”.
- The “Carrot” item has not already been tagged under “Vegetables”.
Untag an item: untag
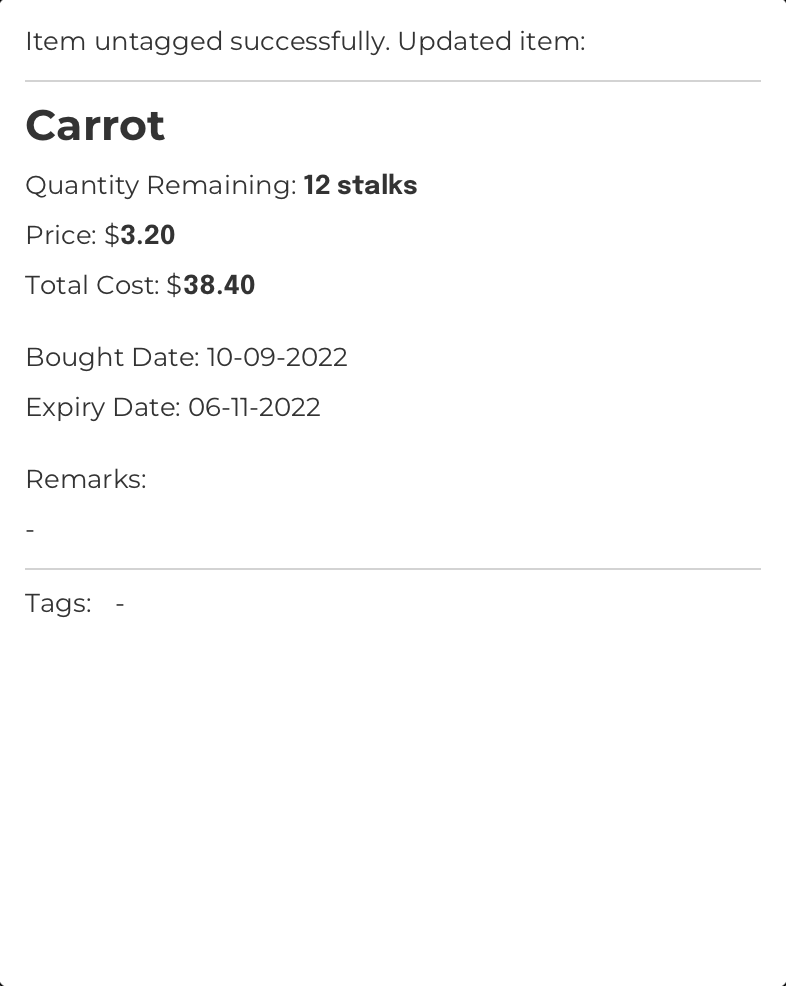
Format: untag INDEX n/TAG_NAME
Untags the item at the specified index
Example:
Command Input Box:
untag 1 n/Vegetables
Assumptions:
- The currently displayed
Item List Box
The region located at the bottom-left of FoodRem’s main window.
Click to view glossary in FoodRem shows the item named “Carrot” at INDEX value 1. - The “Carrot” item is currently tagged under “Vegetables”.
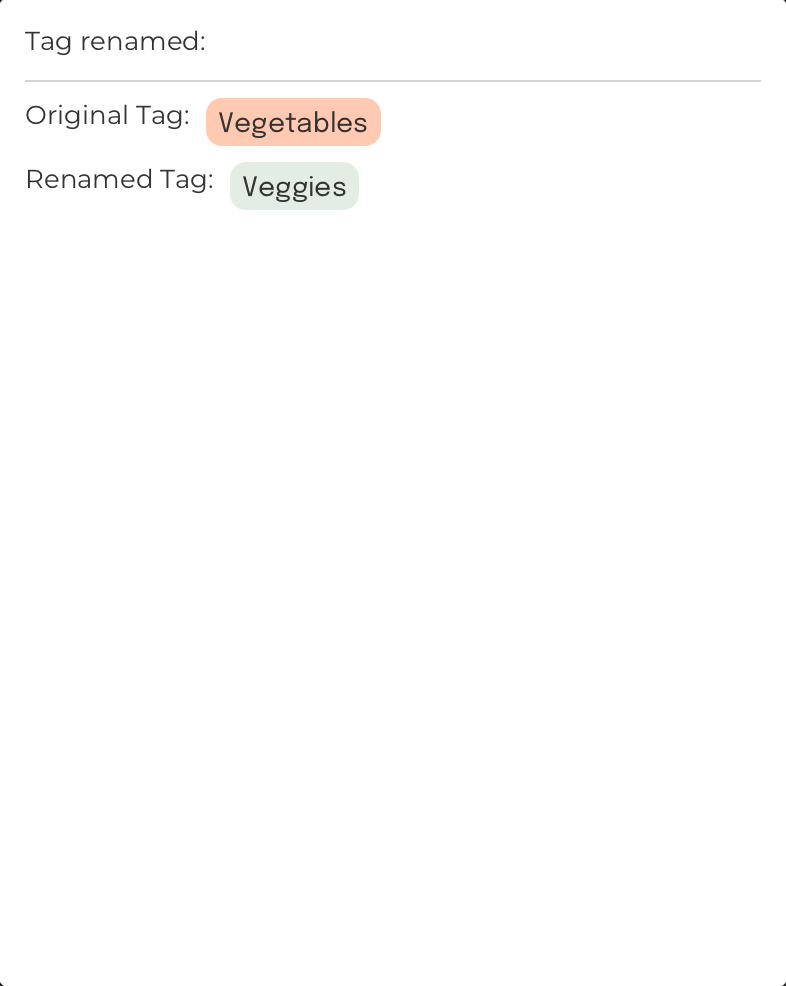
Rename a tag: renametag
Format: renametag n/TAG_NAME n/TAG_NAME
Renames a tag currently in FoodRem
INFO
The first TAG_NAME in the command refers to the current tag you wish to rename while the second TAG_NAME refers to the new name you wish to rename the current tag to.
NOTE
If you encounter an error message saying “This tag name already exists in FoodRem,” it means that the new name you wish to rename the current tag to is already taken by another tag in FoodRem.
Example:
Command Input Box:
renametag n/Vegetables n/Veggies
Assumptions:
- Initially, there exists a tag called “Vegetables”.
- FoodRem does not already contain a tag called “Veggies”.
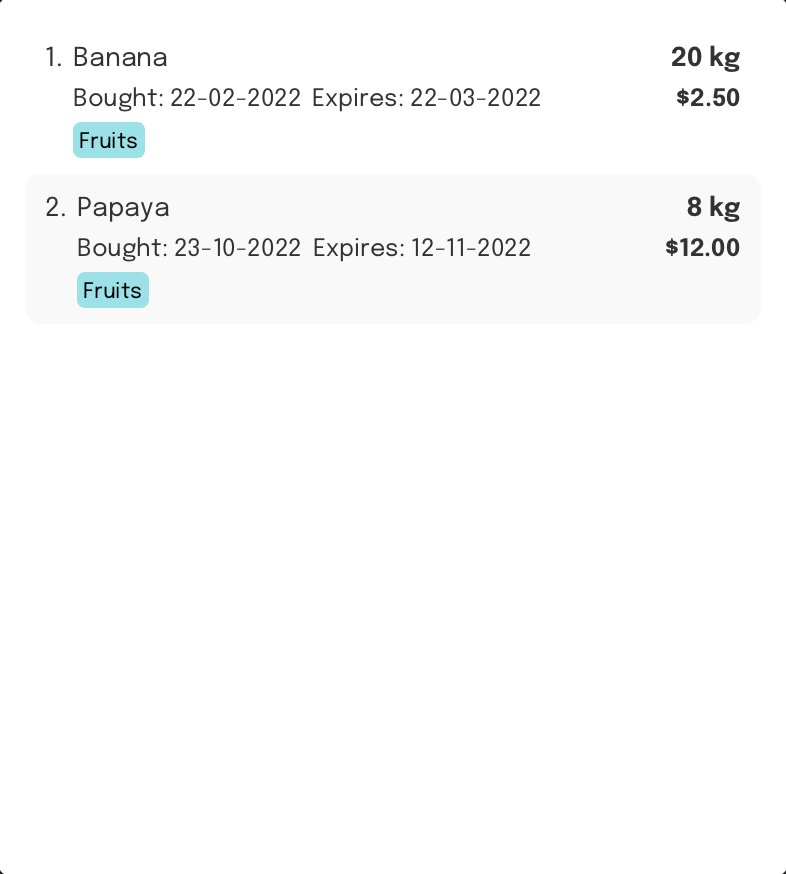
Filter by a tag: filtertag
Format: filtertag n/TAG_NAME
Filters and shows items that contain a specific tag
Example:
Command Input Box:
filtertag n/Fruits
Assumption:
Initially, FoodRem only contains the following items:
- Banana (tagged as “Fruits”)
- Carrot (tagged as “Vegetables”)
- Papaya (tagged as “Fruits”)
- Tomato (tagged as “Vegetables”)
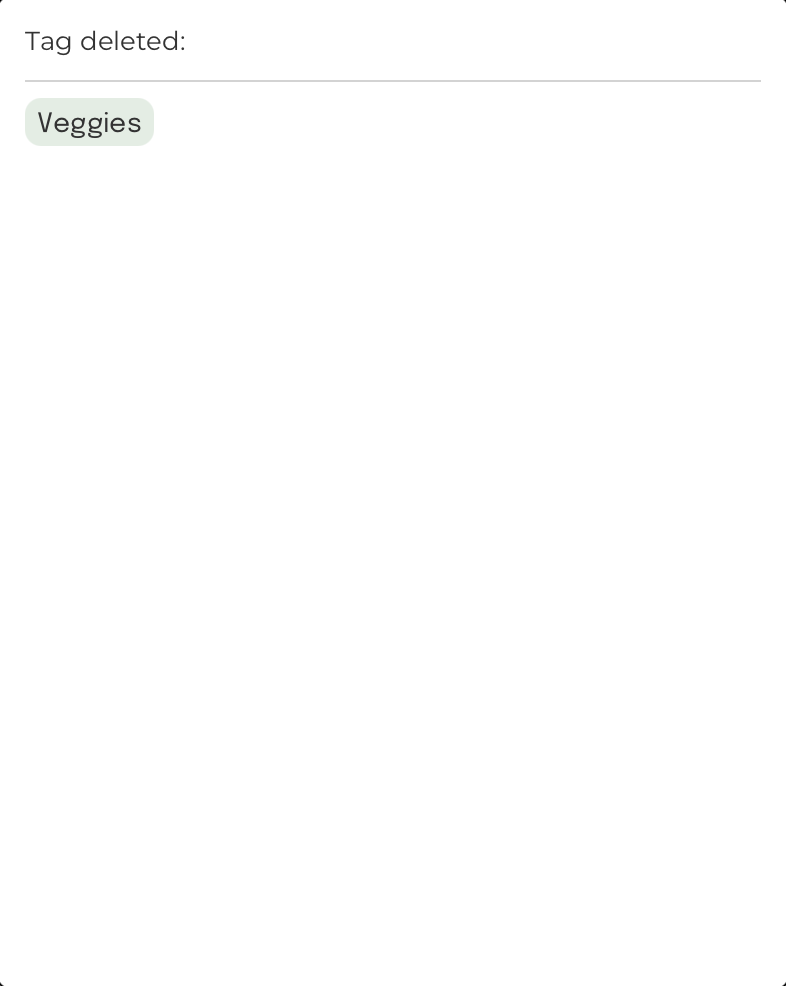
Delete a tag: deletetag
Format: deletetag n/TAG_NAME
Deletes a tag that exists in FoodRem
WARNING
- There is no additional confirmation for deleting a tag that is in use
- Deleting a tag that is already in use will also untag the items under that tag
TIP
You might find the abovementioned Filtertag Command useful to check that a tag is not in use before deleting it.
Example:
Command Input Box:
deletetag n/Veggies
Assumption:
Initially, there already exists a tag called “Veggies”.
Statistics Command
Display statistics: stats
Format: stats
Displays all statistics collected by FoodRem
NOTE
These statistics include:
- Total cost of wasted
items
Represents a thing that is stored and kept track by FoodRem.
Click to view glossary - Top 3 most commonly used
tags
The main method of categorizing items in FoodRem. A tag may be attached to zero or more items.
Click to view glossary in your inventory - Top 3 most costly items in your inventory
The cost of an item is the price of the item multiplied by the quantity of the item in your inventory.
TIP
You can use tags in creative ways to take advantage of these statistics! For example, by tagging items by their suppliers, you can use this command to find out which supplier you rely most on, which may be useful for your business negotiations or decisions!
Example:
Command Input Box:
stats
Assumptions:
- Initially, FoodRem has a few items, one of which is:
- Tomato
- Initially, FoodRem has a few tags, three of which are:
- Fruits
- Meat
- Vegetables
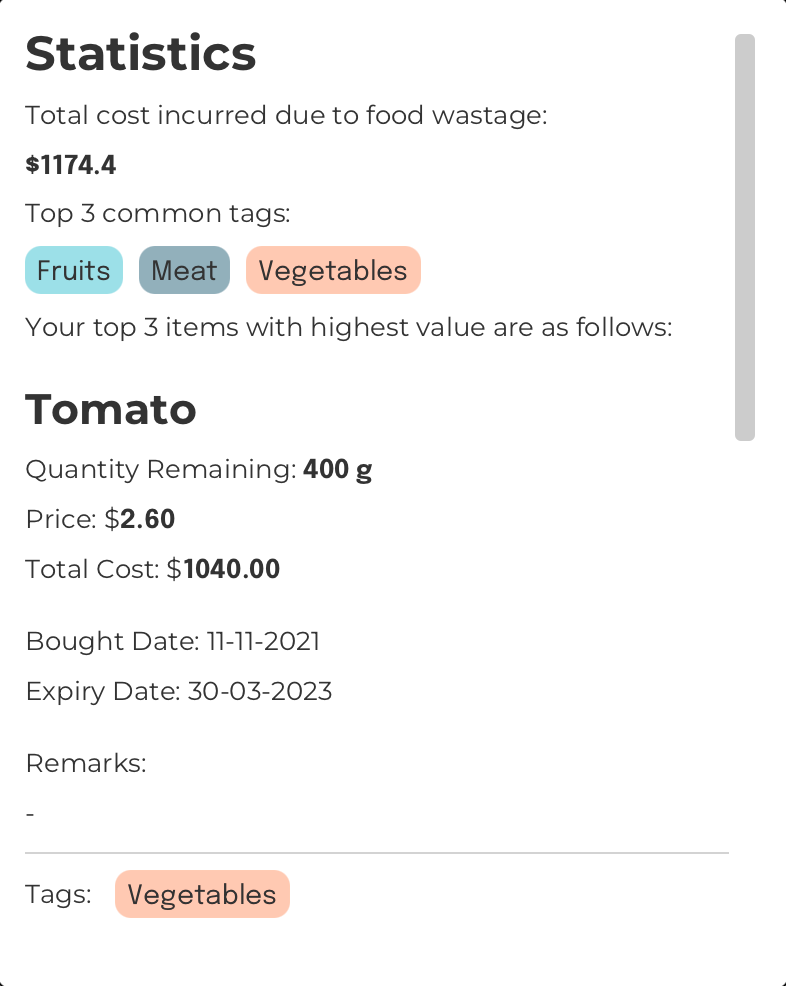
INFO
The above picture only shows a partial view of the Command Output Box. On FoodRem, you can simply scroll down to see the full output! This is the one instance where you need to use a mouse to interact with FoodRem.
General Commands
Receive help during usage: help
Format: help [COMMAND_WORD]
Displays help for FoodRem
NOTE
COMMAND_WORD is strictly any of the following:
- exit
- help
- reset
- dec
- del
- edit
- find
- inc
- list
- new
- rmk
- sort
- view
- deletetag
- filtertag
- listtag
- newtag
- renametag
- tag
- untag
Example:
Command Input Box:
Possible inputs:
help
help del
help help
Help Window:
The
Help Window
A pop-up window containing help information, shown only after calling a help command.
Click to view glossary
will open showing the instructions.
If no COMMAND_WORD was specified, only a general help message will be provided. The general help message shows a list of commands available to the user and a
URL
A hyperlink to a website.
Click to view glossary
to this User Guide.
If a COMMAND_WORD was specified, additional help for that command will be provided.
Reset the application: reset
Format: reset
Clears all items and tags in FoodRem
TIP
You may find this command useful when you start FoodRem for the first time. Initially, FoodRem starts up with some sample data, which, once you have figured out how to use FoodRem, may want to clear so that you can start using it for your own business!
Example:
Command Input Box:
reset
Assumptions:
None

Exit FoodRem: exit
Format: exit
Exits FoodRem
WARNING
This command is the only guaranteed way for the data file to be saved when you exit the application To prevent, always exit the application using this command instead of any other way.
Example:
Command Input Box:
Possible inputs:
exit
Expected Outcomes:
- All FoodRem application windows will close
- Your inventory data is saved.
NOTE
If your inventory data cannot be saved successfully, FoodRem will not close in order to prevent data loss.
Command Summary
Item Commands
| Action | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Create a new item |
|
|
| List all items |
|
|
| Search for an item |
Note: You can provide multiple keywords to find an item. For example, |
|
| Sort all items by name, quantity, unit, bought date, expiry date, price or remark |
|
|
| View the information of an item |
|
|
| Increase the quantity of an item |
|
|
| Decrease the quantity of an item |
|
|
| Edit the information of an item |
|
|
| Add a remark to an item |
|
|
| Delete an item |
|
|
Tag Commands
| Action | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Create a new tag |
|
|
| List all tags |
|
|
| Tag an item |
|
|
| Untag an item |
|
|
| Rename a tag |
|
|
| Delete a tag |
|
|
| Filter items by tag |
|
|
Statistics Command
| Action | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Displays all statistics collected by FoodRem |
|
|
General Commands
| Action | Format | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Shows a help dialog with a list of available commands |
|
|
| Clears all items and tags in FoodRem |
|
|
| Exits FoodRem |
|
|
Troubleshooting
Problem:
The JAR file not launching even after double-clicking the file.
Solution:
- Open your terminal
- Windows:
- The default key combination to launch your terminal is Ctrl+Shift+P
- Mac:
- Use Cmd+Space to open Spotlight Search
- Search for “terminal” and click it to launch.
- Windows:
- Navigate to the location where “foodrem.jar” is stored within your terminal.
- On your terminal, run
java -jar "foodrem.jar"
Problem:
The JAR file not launching in Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
NOTE
WSL does not support GUI applications by default.
Solution:
- Our recommendation is to run FoodRem on Windows and not on WSL.
Problem:
The JAR file not launching in Linux machines running Wayland.
Solution:
INFO
Under the hood, FoodRem uses JavaFX 17 to render the UI for the GUI. Unfortunately, JavaFX 17 has poor support for Wayland which is why FoodRem is unable to support Wayland currently.
- FoodRem is only supported on machines with the following operating systems: Windows, macOS and Linux11. Please use a computer running on these operating systems.
Problem:
Unable to exit/save FoodRem to data file
Solution:
- This error is due to
foodrem.jarbeing started in a protected folder. (Examples of write-protected folders includeC:\WINDOWS\System32in windows and the/etcdir in linux)
Please move thefoodrem.jarfile into another folder in your computer and start FoodRem from that folder.
FAQ
Q: If I do not have Java 17, how do I install it on my computer?
A: You can navigate to this site here and download Java 17 according to your system’s specifications.
Q: Do I need an internet connection to run FoodRem?
A: No, FoodRem can boot up and run all functionalities without an internet connection.
Q: Can I use FoodRem on my mobile device?
A: Unfortunately, FoodRem is only designed to run on your desktop/laptop such that you can use the command line interface.
Q: How do I transfer my data to another computer?
A: Install FoodRem on the other computer and overwrite the empty data file with the data file created by FoodRem in your current computer.
Acknowledgements
FoodRem is a brownfield software project based off AddressBook Level-3, taken under the CS2103T Software Engineering module held by the School of Computing at the National University of Singapore.
Java dependencies:
Documentation dependencies:
Fonts used in FoodRem:
- FoodRem Java App:
- Epilogue by Tyler Finck
- JetBrains Mono by Philipp Nurullin and Konstantin Bulenkov
- Montserrat by Julieta Ulanovsky et al.
- FoodRem Website:
- Epilogue by Tyler Finck
- Source Code Pro by Paul D. Hunt
Other acknowledgments:
- Material Design Icons:
- food-turkey by Colton Wiscombe as FoodRem’s App Icon
- Font Awesome 6 icons:
- book as the “note” admonition icon
- circle-info as the “info” admonition icon
- fire-flame-curved as the “danger” admonition icon
- lightbulb as the “tip” admonition icon
- triangle-exclamation as the “warning” admonition icon
- Octicons:
- git-merge for the PR badge used in the project PPPs
- issue-closed for the issue badge used in the project PPPs
- Code acknowledgements:
- Custom link fragment checker adapted from the World Wide Web Consortium
- Pure CSS auto-incrementing heading counters adapted from @gvgramazio on StackOverflow
- PDF styling of HTML pages following Michael Perrin’s tutorial
- Pure liquid admonitions adapted from @kimkyunghwan21 on GitHub
- Pure liquid HTML table-of-contents from @allejo on GitHub
- Miscellaneous:
- Docusaurus for admonition colors and styling
- GitHub for “PR merged” and “issue closed” colors used in PPP badges
- SchemeColor for admonition colors
Glossary
A
Admonitions
Admonition boxes (or simply “admonitions”) are coloured boxes containing highlighted pieces of text.
For details on the various types of various types of admonitions used in FoodRem, see the section on Admonition Boxes.
B
BOUGHT_DATE (Placeholder)
The BOUGHT_DATE is the date indicating when an item was bought.
To view more information (constraints, examples, etc.), refer to the Placeholders table.
Bought Date
Date where an item was purchased. Bought date is in the format “day-month-year”, represented in the “dd-mm-yyyy” format.
C
COMMAND_WORD (Placeholder)
The COMMAND_WORD is a text indicating a command word of a command
To view more information (constraints, examples, etc.), refer to the Placeholders table.
Command
A feature or function that FoodRem can perform.
Command Input Box
The region located at the top-left of FoodRem’s main window.
To view more information, refer to the Layout section of the User Guide.
Command Line
The typing interface that you use to interact with FoodRem. It is represented as the box where you type in commands.
Command Output Box
The region located at the right half of FoodRem’s main window.
To view more information, refer to the Layout section of the User Guide.
D
Delimiter
A sequence of one or more characters for specifying the boundary between separate, independent regions in plain text.
E
EXPIRY_DATE (Placeholder)
The EXPIRY_DATE is the date indicating when an item will expire.
To view more information (constraints, examples, etc.), refer to the Placeholders table.
Expiry Date
Date where an item spoils, expires, or becomes unusable. Expiry date is in the format “day-month-year”, represented in the “dd-mm-yyyy” format.
F
Flag
A marker or delimiter signifying a potentially optional argument to a command. For example on FoodRem, in the syntax n/ITEM_NAME , n/ is the flag.
G
Graphical User Interface
A Graphical User Interface is a graphics-based interface that uses icons, menus and a mouse (to click on the icon or pull down the menus) to manage interaction with the system. In FoodRem, this presents as the window that appears when launching it.
H
Help Window
A pop-up window containing help information, shown only after calling a help command.
To view more information, refer to the Layout section of the User Guide.
I
INDEX (Placeholder)
The INDEX of an item is the number to the left of the item name in the List Component.
To view more information (constraints, examples, etc.), refer to the Placeholders table.
ITEM_NAME (Placeholder)
The ITEM_NAME is the name we use to identify an item.
To view more information (constraints, examples, etc.), refer to the Placeholders table.
Input
The text that a user would enter into FoodRem.
Item
Represents a thing that is stored and kept track by FoodRem.
Example: Creating a potato item
new n/potato
Item List Box
The region located at the bottom-left of FoodRem’s main window.
To view more information, refer to the Layout section of the User Guide.
K
KEYWORD (Placeholder)
The KEYWORD is the text we use search for an item.
To view more information (constraints, examples, etc.), refer to the Placeholders table.
O
Operating System (OS)
Operating System (OS) of the computer which manages the software and hardware on the computer.
Output
The result of calling a Command. Results are displayed in the GUI, here: (ADD SCREENSHOT)
P
PRICE (Placeholder)
The PRICE is the number representing the cost of one unit of an item.
To view more information (constraints, examples, etc.), refer to the Placeholders table.
Parameter
Parameters identify values passed into your Commands. For example, when calling add n/ItemName, the parameter here is n/ItemName.
Placeholder
Placeholders in FoodRem refers to the UPPER_CASE words that appear after flags in commands that can be replaced by user input supplied. For example in n/ITEM_NAME, ITEM_NAME is a placeholder.
Purchasing Manager
A purchasing manager, also known as a purchasing director or supply manager, heads a team responsible for procuring goods and services for resale or company use.
Q
QUANTITY (Placeholder)
The QUANTITY is the number representing the amount of an item.
To view more information (constraints, examples, etc.), refer to the Placeholders table.
Quantity
The amount/count of item(s) kept track by FoodRem.
R
REMARKS (Placeholder)
The REMARKS of an item is a note that you can add to an item.
To view more information (constraints, examples, etc.), refer to the Placeholders table.
S
Substring
A contiguous sequence of characters (letters) that form a part (or a whole) string of text.
Example: “ca” is a substring of “ca”, “cat” and “thecat”, but not “ac”.
Syntax
The structure of statements users type into the Command Line.
T
TAG_NAME (Placeholder)
The TAG_NAME is the term we use to identify an item.
To view more information (constraints, examples, etc.), refer to the Placeholders table.
Tag
The main method of categorizing items in FoodRem. A tag may be attached to zero or more items.
U
UNIT (Placeholder)
The UNIT is a text indicating the unit of an item.
To view more information (constraints, examples, etc.), refer to the Placeholders table.
URL
A hyperlink to a website.